How Pain Relievers Can Affect Blood Sugar Levels
Services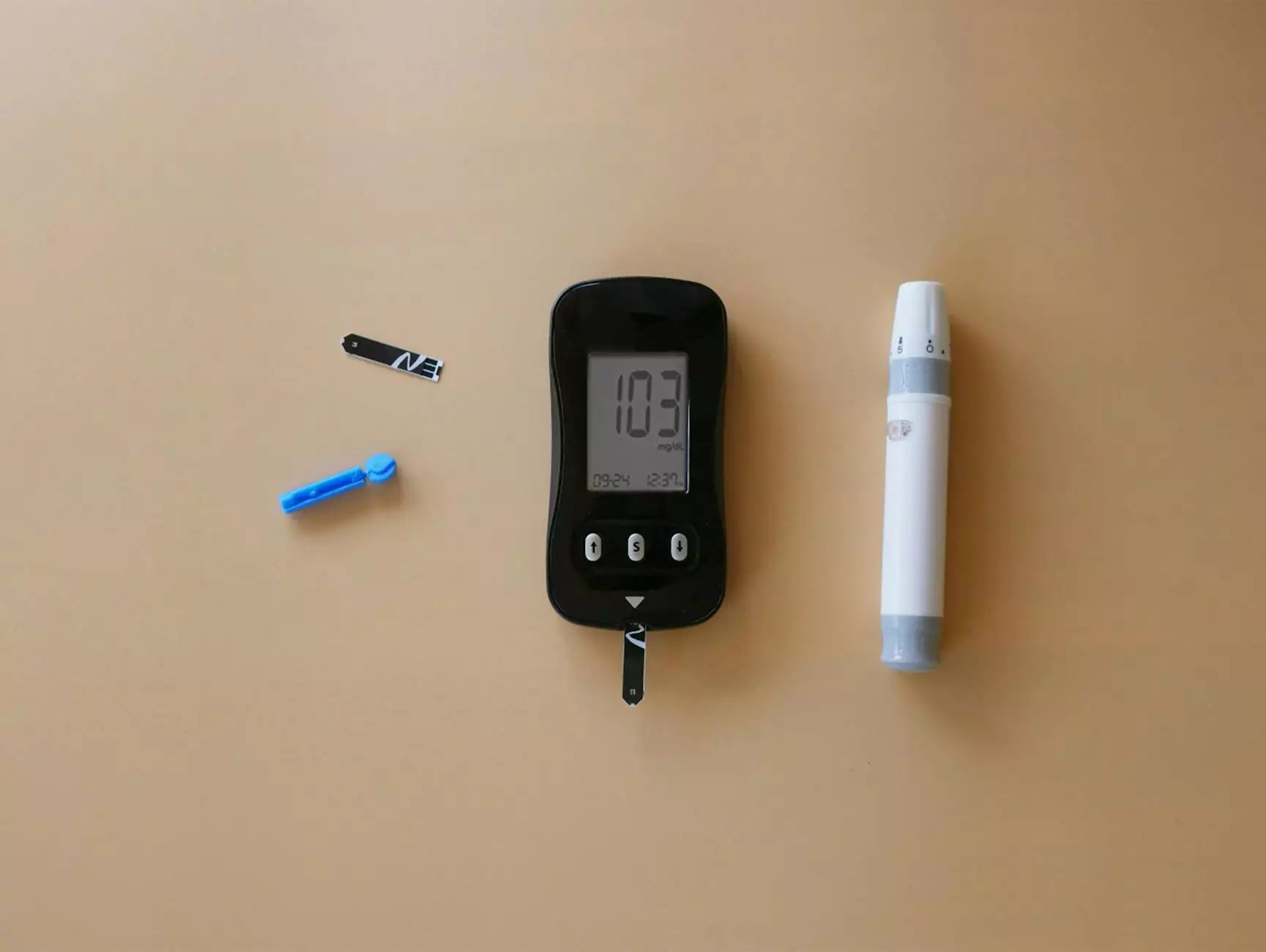
Introduction
Welcome to Benjamin Shettell, MD - your trusted source for reliable healthcare information. In this article, we will explore the impact of pain relievers on blood sugar levels, specifically focusing on their effects on individuals with diabetes.
The Relationship Between Pain Relievers and Blood Sugar Levels
For individuals managing diabetes, it is essential to understand how various medications can potentially affect their blood sugar levels. Pain relievers, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and opioids, can have both direct and indirect impacts on blood glucose.
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Many people rely on NSAIDs to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. However, it's important to note that certain NSAIDs can potentially cause fluctuations in blood sugar levels, especially in individuals with diabetes. The specific mechanism of action varies among different NSAIDs, but some research suggests that these medications may impair insulin sensitivity and increase the risk of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
If you have diabetes and regularly use NSAIDs, it is crucial to monitor your blood sugar levels closely and consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance based on your unique medical condition.
Opioids
Opioid medications are commonly prescribed for managing moderate to severe pain. While opioids themselves may not directly impact blood sugar levels, certain side effects can indirectly affect glucose control. One example is constipation, a common side effect of opioids, which can contribute to delayed gastric emptying and potentially impact blood glucose levels.
It is vital to work closely with your healthcare provider when using opioids for pain management, as they can provide recommendations and strategies to minimize the impact on your blood sugar levels.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels While Taking Pain Relievers
If you have diabetes and need to take pain relievers for an acute or chronic condition, it is crucial to take certain precautions to manage your blood sugar levels effectively. Here are some tips:
1. Regular Glucose Monitoring
Monitoring your blood sugar levels regularly is essential in understanding how pain relievers may affect your glucose control. Keep a record of your readings and share them with your healthcare provider. This can help them make informed decisions regarding your treatment plan.
2. Consult with Your Healthcare Provider
Your healthcare provider is your best source for personalized guidance. Inform them about your diabetes and the pain relievers you are taking. They can offer tailored advice on managing medications, adjusting insulin dosages (if necessary), and monitoring your blood sugar levels.
3. Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
A healthy diet and regular exercise play a significant role in managing diabetes. Adhering to a balanced diet and engaging in physical activity can help counteract any potential negative effects of pain relievers on blood sugar levels. Follow your healthcare provider's recommendations for meal planning, portion control, and incorporating exercise into your daily routine.
4. Consider Alternative Pain Management Options
Depending on your condition, there might be alternative pain management approaches that are less likely to impact blood sugar levels. Discuss these options with your healthcare provider to determine whether they may be suitable for you.
5. Educate Yourself
Stay informed about the potential effects of pain relievers on blood sugar levels. Websites like Benjamin Shettell, MD provide valuable resources and articles to help you make well-informed decisions about your healthcare.
Conclusion
Managing blood sugar levels is a crucial aspect of diabetes care. Understanding how pain relievers can affect your glucose control is essential for individuals with diabetes who require pain management. By staying informed, working closely with your healthcare provider, and taking necessary precautions, you can balance your pain relief needs while maintaining optimal blood sugar levels.