Unveiling Sun Poisoning: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and When to Seek Medical Help
Services
Welcome to Benjamin Shettell, MD, your trusted source of comprehensive health information. In this article, we will dive deep into the topic of sun poisoning, exploring its causes, symptoms, available treatments, and when it is crucial to seek medical assistance. We aim to provide you with in-depth knowledge and guidance on managing sun poisoning effectively.
Understanding Sun Poisoning
Sun poisoning, also known as severe sunburn or photodermatitis, is a severe form of sunburn caused by prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. This condition goes beyond the typical redness and skin irritation associated with a regular sunburn, requiring prompt attention and proper treatment to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
Common Causes of Sun Poisoning
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of sun poisoning. The primary cause is prolonged exposure to UV radiation without adequate sun protection. This can occur during outdoor activities such as sunbathing, hiking, or participating in sports without proper sunblock or protective clothing.
Additionally, certain medications, such as antibiotics, diuretics, and birth control pills, can increase vulnerability to sunburn and sun poisoning. It's essential to consult with your healthcare provider if you are taking any medications that may heighten sun sensitivity.
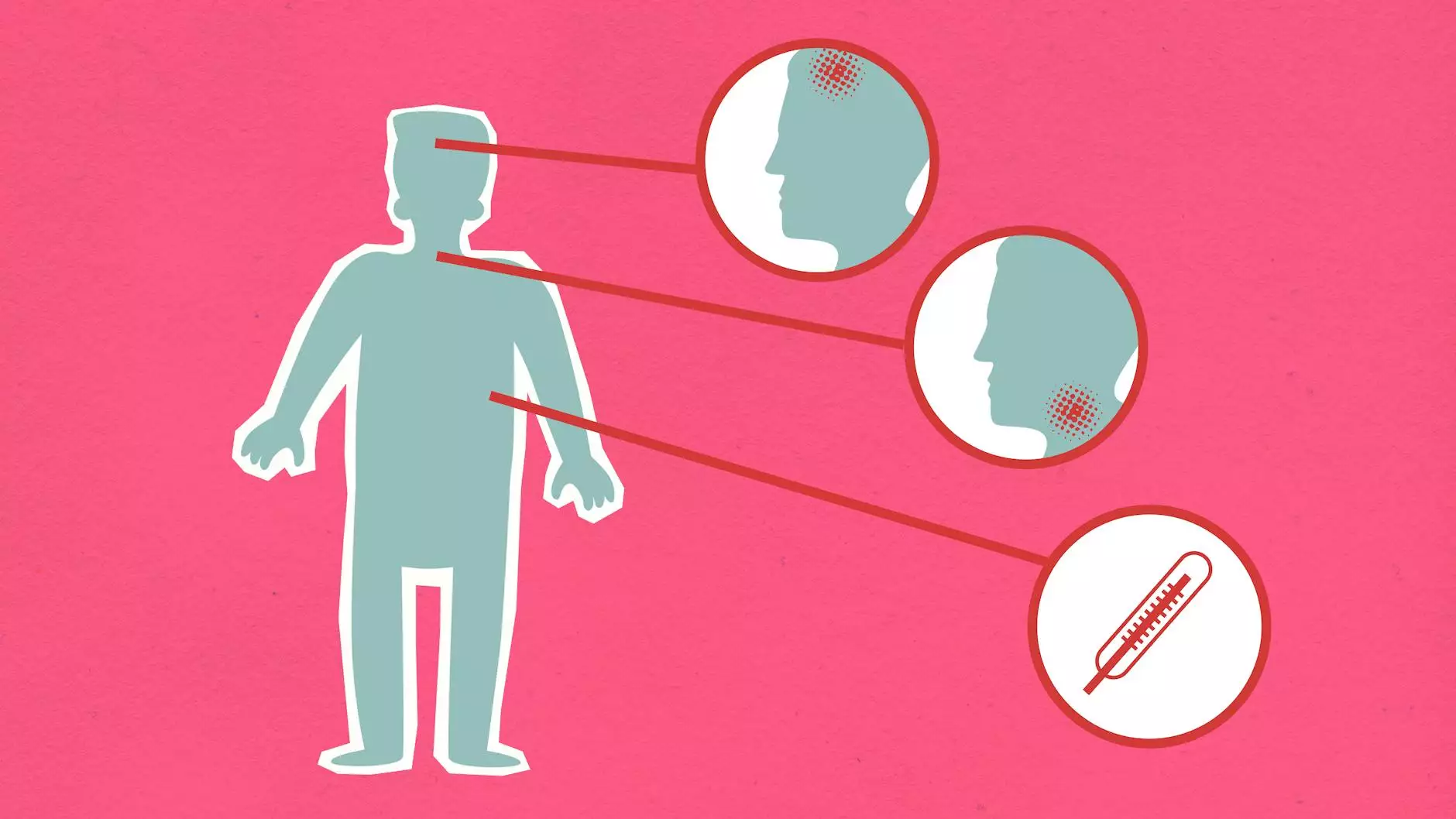
Recognizing the Symptoms
The symptoms of sun poisoning may vary from person to person, but there are common signs to watch out for. These can include severe skin redness, blistering, swelling, pain or tenderness in the affected area, headache, dizziness, nausea, fever, and chills. In extreme cases, sun poisoning can even lead to dehydration and heatstroke.
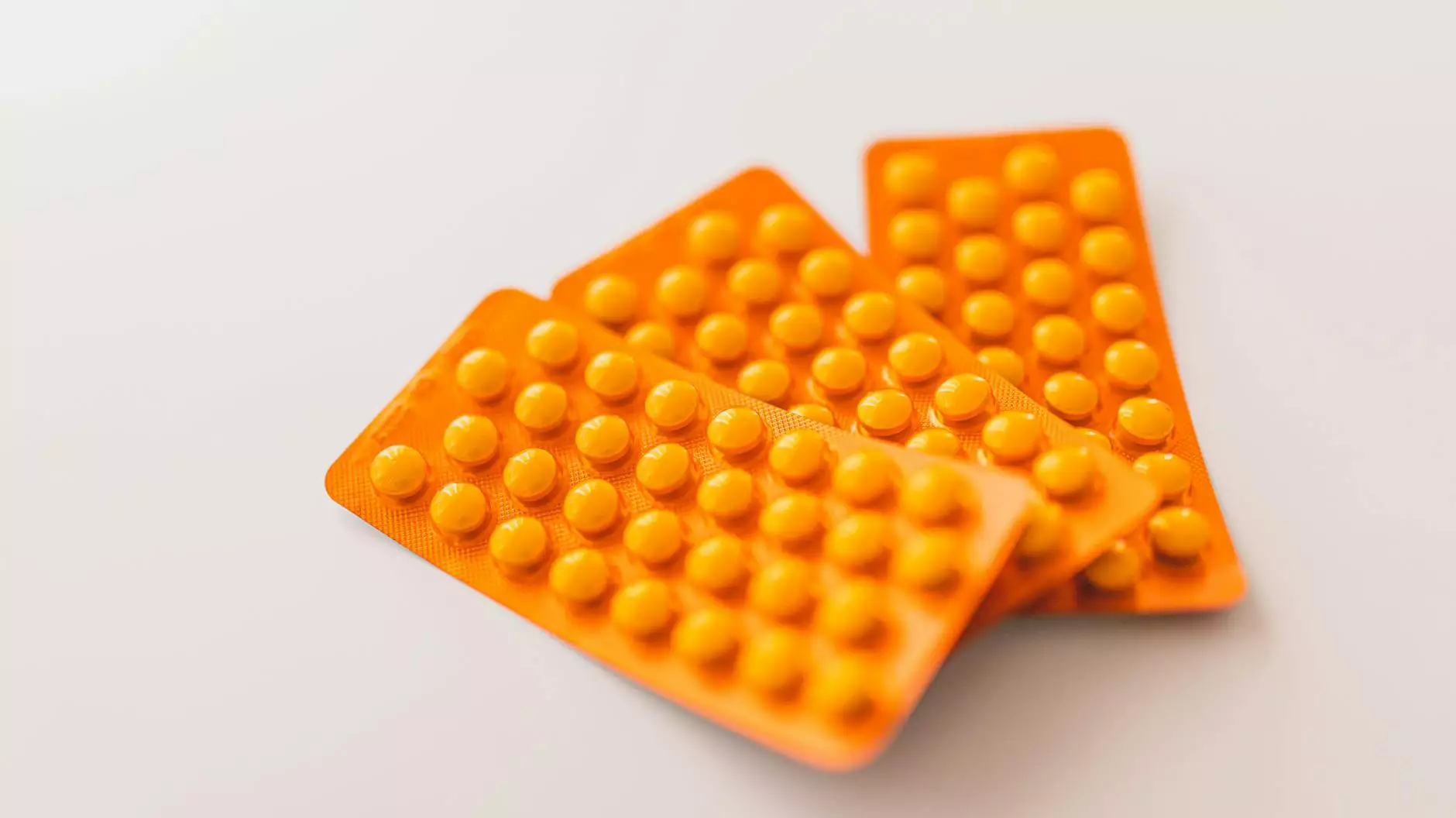
Treatment Options for Sun Poisoning
If you suspect you may be experiencing sun poisoning, it's crucial to take immediate action to alleviate symptoms and promote healing. Here are some recommended treatment options:
- Cool Compresses: Apply cool compresses or take cool baths to soothe and cool down the affected skin.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration, especially if you are experiencing fever or nausea.
- Aloe Vera: Apply aloe vera gel or lotion to the affected area to promote healing and reduce inflammation.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Topical Steroids: In some cases, a healthcare professional may prescribe topical steroid creams or ointments to reduce itching and inflammation.
However, it's important to remember that these are general suggestions, and the best course of treatment can vary depending on the severity of your sun poisoning symptoms. It is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance.
When to Seek Medical Help
Although most cases of sun poisoning can be effectively managed at home, there are situations where medical assistance is necessary. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- Severe blistering: If your sunburn blisters and covers a large area of your body.
- Significant pain: If you are experiencing severe pain that is not relieved with over-the-counter medications.
- Fever and chills: If you develop a fever over 102°F (38.9°C) or experience severe chills.
- Dizziness and confusion: If you feel lightheaded, dizzy, or confused.
- Dehydration: If you are unable to drink fluids or if you feel extremely thirsty.
These symptoms could indicate a more severe condition requiring immediate medical attention.
Preventing Sun Poisoning
Prevention is always better than cure when it comes to sun poisoning. Follow these tips to protect yourself from excessive sun exposure:
- Apply Sunscreen: Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, and remember to reapply every two hours or after swimming or excessive sweating.
- Seek Shade: Take breaks from direct sunlight by seeking shade, particularly during peak hours (10 am to 4 pm) when UV rays are strongest.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Cover exposed skin with lightweight and breathable clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts, trousers, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to maintain hydration and prevent heat-related illnesses.
By following these preventative measures, you can reduce your risk of sunburn and sun poisoning significantly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sun poisoning is a severe form of sunburn that requires immediate attention and proper treatment. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and knowing when to seek medical help are vital for managing sun poisoning effectively.
Remember to practice proper sun protection, take necessary precautions, and consult with a healthcare professional if you experience severe or prolonged sun poisoning symptoms. Benjamin Shettell, MD is committed to providing you with accurate health information to help you make informed decisions about your well-being.