Mastering Wheat Weevil Control: Essential Strategies for Farmers
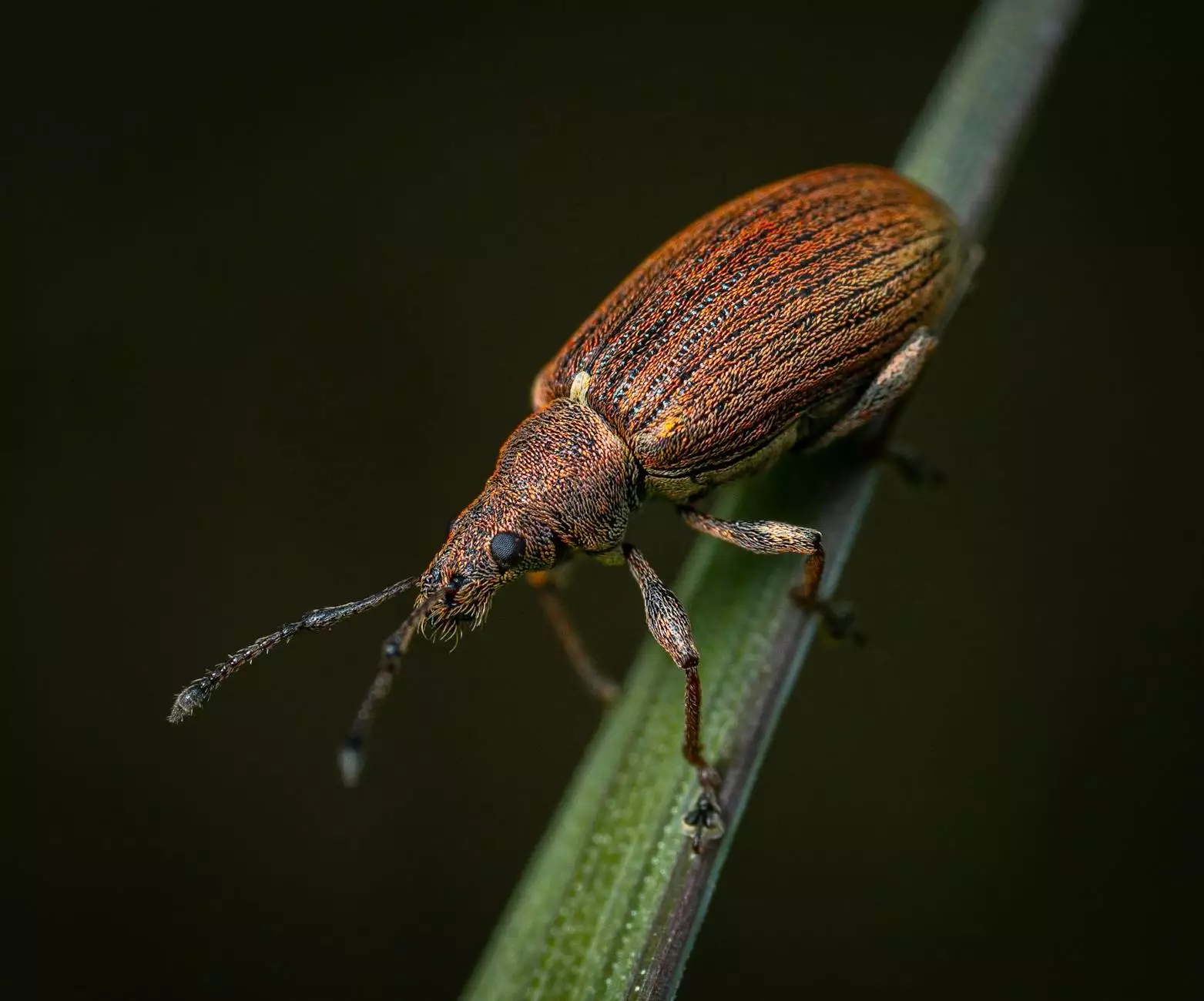

At TSGC Inc., we understand the critical role that effective pest management plays in ensuring sustainable farming practices. One of the most notorious pests affecting grain storage is the wheat weevil (Sitophilus granarius), which can wreak havoc on wheat and other stored grains if not adequately controlled. This article dives deep into the strategies for wheat weevil control, offering farmers actionable insights to protect their harvests and maintain profitability.
Understanding Wheat Weevils: Identification and Biology
The first step in controlling any pest is understanding it. Wheat weevils are small, brownish beetles that typically measure between 2.5 to 4 mm in length. They can be identified by their long snouts and characteristic punctuated holes in grains.
Life Cycle of the Wheat Weevil
- Egg Stage: Female weevils lay eggs in individual kernels of wheat. Each female can lay up to 200 eggs in her lifetime.
- Lara Stage: After a few days, the eggs hatch into larvae, which burrow into the grain kernel, feeding on the starch and nutrient-rich parts.
- Pupal Stage: The larvae mature into pupae inside the grain, eventually emerging as adult weevils, completing their lifecycle.
Impact of Wheat Weevils on Agricultural Productivity
The presence of wheat weevils can lead to severe damage. When larvae infest kernels, they consume the internal contents, leading to weight loss, reduced nutritional quality, and in some cases, complete spoilage. A heavy infestation can result in substantial economic losses for farmers, making wheat weevil control crucial.
Effective Strategies for Wheat Weevil Control
Implementing a combination of prevention, monitoring, and control techniques is essential for effective management of wheat weevils.
Preventive Measures
To prevent infestation, farmers should consider the following strategies:
- Proper Storage: Use airtight containers for storing grain. Ensure that storage facilities are clean and dry to inhibit weevil reproduction.
- Temperature Control: Store grains in cool, dry conditions. Wheat weevils thrive in warm, moist environments; keeping the storage area cool can inhibit their activity.
- Regular Inspection: Conduct frequent checks of stored grains to detect early signs of infestation, such as surface damage or adult weevil presence.
Monitoring Techniques
Monitoring the levels of infestation is vital. Farmers can employ the following techniques:
- Pheromone Traps: Use traps that contain sex pheromones to attract and capture adult weevils, helping track population levels.
- Visual Inspections: Regularly check for adult weevils and larvae. Observations of grain damage or unusual dust can signal an infestation.
Control Methods
If infestation is detected, the following control methods can be implemented:
- Physical Control: Remove and dispose of heavily infested grains. Use vacuuming techniques to clean storage areas thoroughly.
- Chemical Control: Insecticides can be applied, but it is crucial to follow guidelines strictly to ensure safety and prevent resistance. Consider consulting with a pest management professional.
- Biological Control: Explore natural predators such as parasitic wasps that can help reduce weevil populations.
Integrating Technology in Wheat Weevil Control
Advancing technology provides farmers with innovative tools for wheat weevil control. Here are some cutting-edge approaches:
- Remote Sensing: Utilize drones equipped with imaging technology to monitor grain storage facilities for potential infestations.
- Data Analytics: Use analytics software to track pest patterns and predict high-risk periods for infestations, allowing for proactive measures.
Case Studies: Successful Wheat Weevil Control
Real-world examples illustrate the effectiveness of comprehensive wheat weevil control strategies:
Case Study 1: A Family Farm
On a family-owned wheat farm in the Midwest, the introduction of pheromone traps resulted in a 75% reduction in wheat weevil populations over two growing seasons. Regular monitoring and temperature adjustments in storage facilities played a key role in this success.
Case Study 2: Large-Scale Grain Processing Facility
A grain processing company implemented a combination of physical removal and biological control methods. By introducing natural predators and regularly cleaning storage areas, they managed to keep pest levels below economic thresholds, leading to increased profitability.
Frequently Asked Questions About Wheat Weevil Control
What are the symptoms of a wheat weevil infestation?
Common symptoms include:
- Punctured grain kernels
- Visible adult weevils and larvae
- Increased powdery dust around stored grains
Can I eat grain infested with wheat weevils?
While the grain may not be harmful to consume if cooked, it is not advisable. Infested grain often has reduced quality and may harbor pathogens.
How can I minimize the use of pesticides while controlling weevils?
Focus on preventive measures like proper storage, regular inspections, and integrating biological control methods to limit pesticide usage.
Conclusion: The Future of Wheat Weevil Control
As agriculture continues to evolve, wheat weevil control methods must adapt to incorporate sustainable practices. At TSGC Inc., we advocate for a holistic approach combining technology and traditional methods. By staying informed and proactive, farmers can protect their crops and ensure long-term productivity and sustainability.
For more information on our services in Farm Equipment Repair and Farming Equipment, or to inquire about effective pest management solutions that cater to your specific needs, reach out to us at TSGC Inc. today!