Diet and Osteoporosis: What We Eat Can Affect Bone Health
Services
Welcome to Benjamin Shettell, MD, your trusted source for comprehensive health information. In this article, we will explore the vital connection between diet and osteoporosis. Understanding the impact of nutrition on bone health is crucial to effectively prevent and manage this common condition that affects millions around the world.
The Importance of Bone Health
Bone health is essential for overall well-being, as our skeletal system provides vital support and protection for our organs, keeps our body upright, and enables mobility. Osteoporosis, characterized by low bone density and deterioration, can lead to an increased risk of fractures and reduced quality of life.
Research has demonstrated that diet plays a significant role in maintaining strong and healthy bones. By incorporating proper nutrition, we can slow down bone loss, promote bone formation, and reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
The Key Nutrients for Optimal Bone Health
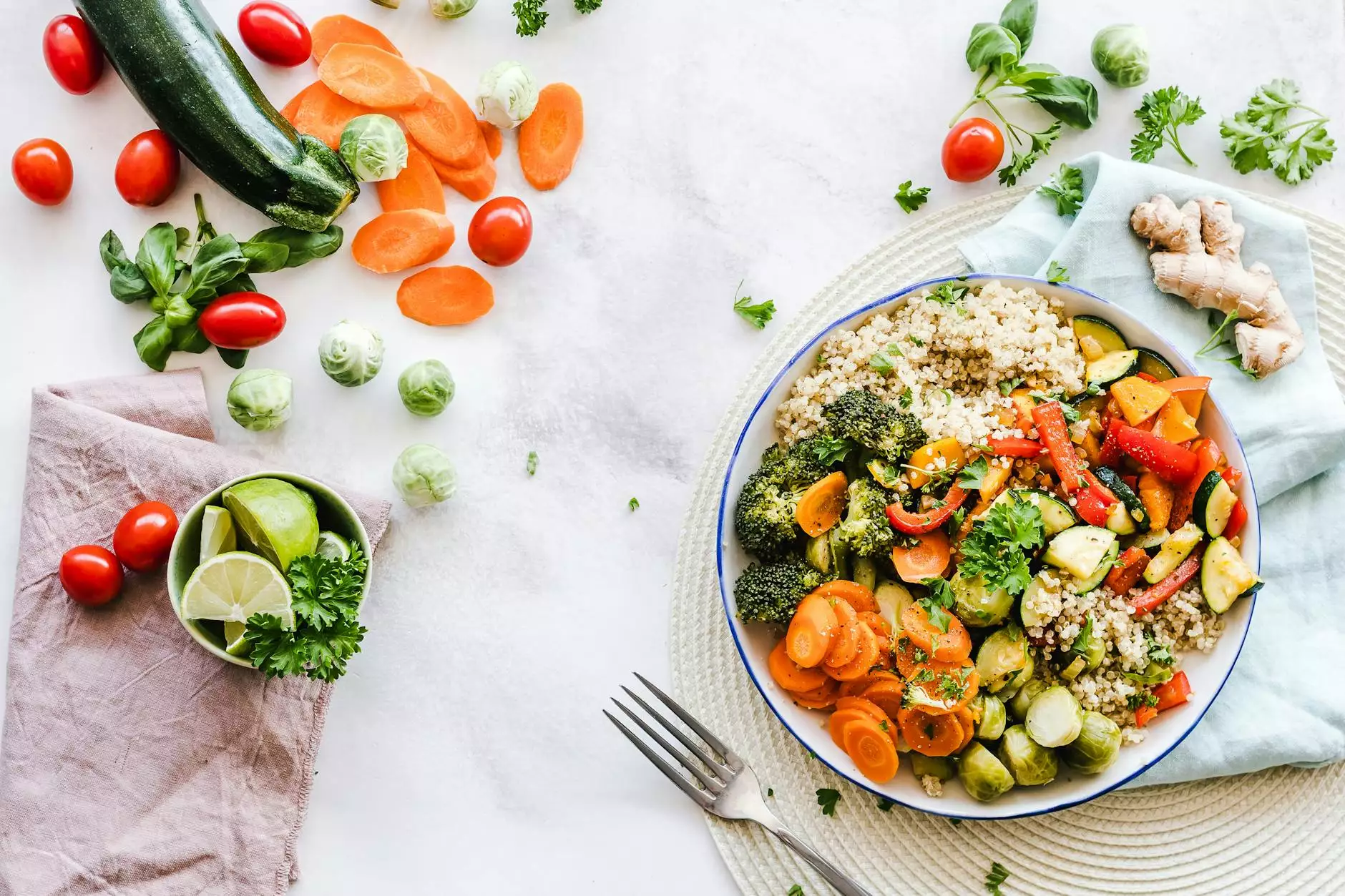
1. Calcium: Calcium is a fundamental mineral that contributes to bone strength and density. Incorporate calcium-rich foods into your diet, such as milk, yogurt, cheese, leafy greens, and fortified plant-based milk alternatives. Aim for the recommended daily intake of 1000-1200 mg of calcium, depending on age and gender.
2. Vitamin D: Vitamin D is crucial for calcium absorption and bone metabolism. Exposure to sunlight is the primary source of vitamin D, and it can also be obtained through certain foods like fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified products. In cases of deficiency, supplementation may be necessary.
3. Magnesium: Magnesium supports bone health by assisting with calcium absorption and promoting bone density. Include magnesium-rich foods in your diet, such as nuts, seeds, legumes, whole grains, and green leafy vegetables.
4. Vitamin K: Vitamin K plays a vital role in regulating bone mineralization and reducing fractures. It can be found in abundance in leafy greens, such as spinach, kale, and broccoli, as well as in fermented foods like sauerkraut and natto.
The Impact of Diet on Bone Health
1. High Acidic Foods: Consuming a diet high in acidic foods, like processed meats, refined grains, and carbonated beverages, may contribute to calcium loss from bones. Minimize excessive consumption of these foods to protect bone health.
2. Sodium Intake: High sodium intake can lead to increased calcium excretion through urine, thereby impacting bone density. Limiting the consumption of processed and packaged foods, which are typically high in sodium, is recommended.
3. Protein Intake: Protein is an essential component of bone structure. Ensure an adequate intake of high-quality protein sources such as lean meats, fish, dairy, legumes, and plant-based proteins like tofu and tempeh.
4. Caffeine and Alcohol: Excessive intake of caffeine and alcohol can interfere with calcium absorption and increase the risk of osteoporosis. Moderation is key when consuming these beverages to safeguard bone health.
Creating a Bone-Healthy Diet Plan
Consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian is beneficial in developing a personalized bone-healthy diet plan. They can assess your nutritional needs, offer guidance on portion sizes, and incorporate foods rich in the above-mentioned nutrients into your meals.
It is important to engage in regular physical activity, as exercise, particularly weight-bearing and strength-training exercises, is crucial for bone health. Combining a balanced diet with an active lifestyle can optimize your bone health and reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
At Benjamin Shettell, MD, we understand the significance of diet in maintaining strong bones. Our team of experts is dedicated to providing comprehensive osteoporosis treatment and personalized guidance on nutrition and lifestyle modifications. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you build a solid foundation for lifelong bone health.