Ganglion Cyst: Frequently Asked Questions
FAQ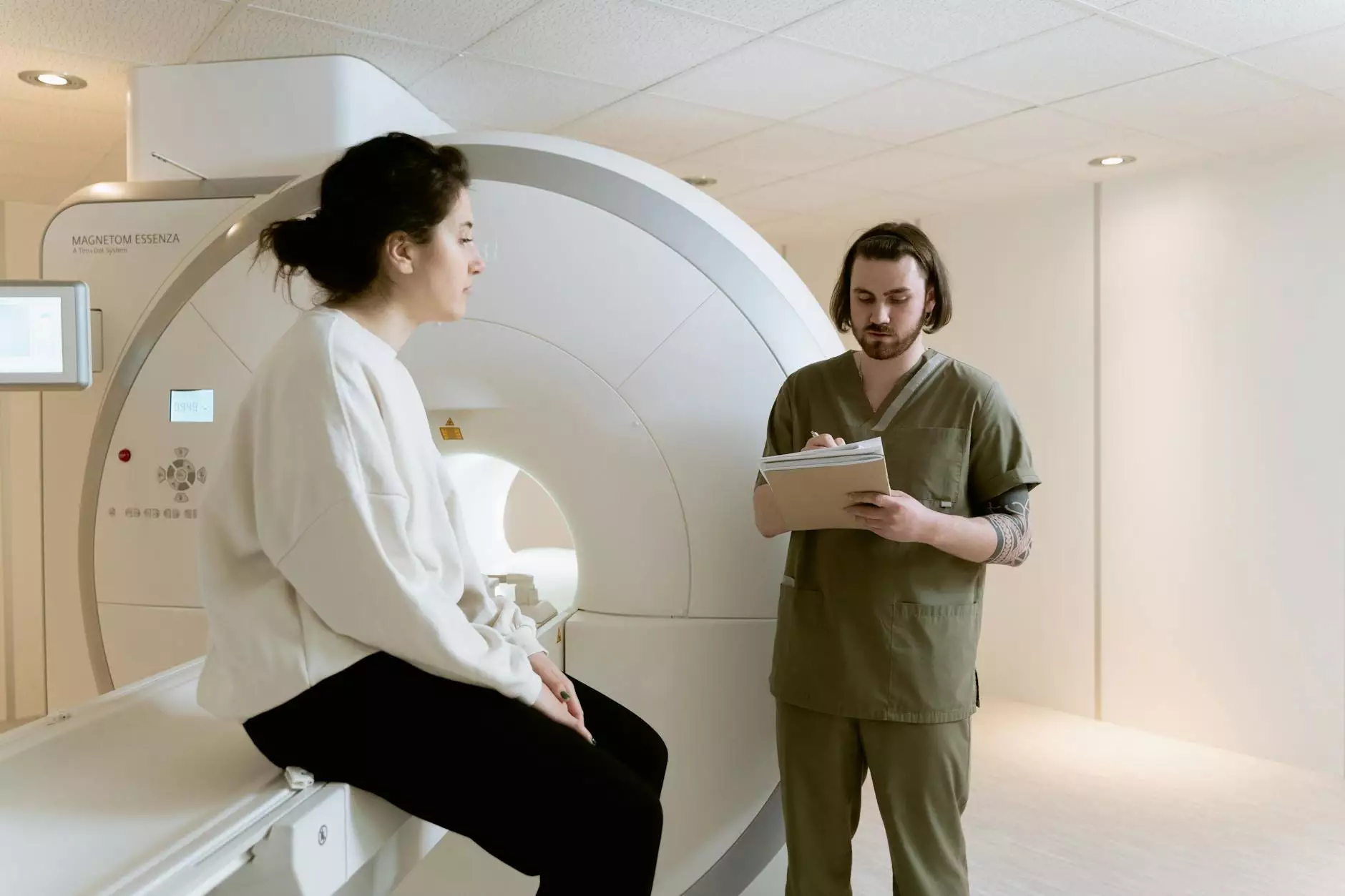
What is a Ganglion Cyst?
A ganglion cyst is a noncancerous lump or mass that usually forms along the joints or tendons of the wrists, hands, fingers, ankles, or feet. It is typically filled with a clear, jelly-like fluid and may feel firm or spongy to the touch. Ganglion cysts are the most common type of noncancerous soft tissue swelling in the hands and wrists.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of ganglion cysts is unknown, but they often develop due to joint or tendon irritation or injury. Certain risk factors may increase the likelihood of developing a ganglion cyst, such as repetitive movements or activities, arthritis, or previous joint or tendon injuries.
Symptoms
Ganglion cysts are usually painless, but they can cause discomfort if they press on nearby nerves or interfere with joint movement. Common symptoms include:
- A visible lump or swelling
- Tenderness or aching sensation
- Difficulty with joint movement
- Numbness or tingling in nearby fingers or toes
Diagnosis
When you visit Benjamin Shettell, MD, for evaluation, he will review your medical history, conduct a physical examination, and may order additional tests such as imaging studies (X-ray, MRI, ultrasound) to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options
The treatment for ganglion cysts depends on various factors such as the size, location, symptoms, and your overall health. Dr. Shettell will discuss the available treatment options with you, which may include:
- Watchful waiting: If the cyst is small, painless, and not causing any functional issues, your doctor may recommend monitoring it rather than intervention.
- Aspiration: Draining the fluid from the cyst with a needle can provide temporary relief. However, cysts have a tendency to recur.
- Surgical removal: This involves a minor surgical procedure to remove the cyst and the associated joint or tendon capsule. Surgery may be recommended if the cyst is large, causing significant pain or functional impairment, or if nonsurgical treatments fail.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
After aspiration or surgical removal, you may need to immobilize the area with a splint or brace to allow proper healing. Dr. Shettell will provide specific instructions for post-treatment care, including wound care, pain management, and when to start gentle exercises or physical therapy, if necessary. It is important to follow these instructions to optimize your recovery.
Prevention
While ganglion cysts cannot always be prevented, certain measures may help reduce the risk of their development or recurrence. These include avoiding repetitive joint movements or activities that strain the affected area and maintaining overall joint and tendon health through regular exercise and proper ergonomics.
Contact Benjamin Shettell, MD
If you have a ganglion cyst or any concerns related to your musculoskeletal health, contact Benjamin Shettell, MD, and his experienced team. They provide comprehensive evaluation, personalized treatment plans, and exceptional care to help you achieve optimal musculoskeletal health and overall well-being.